Components
Viewport
this is viewport snippet using bubbletea and lipgloss.
Vertical Viewport
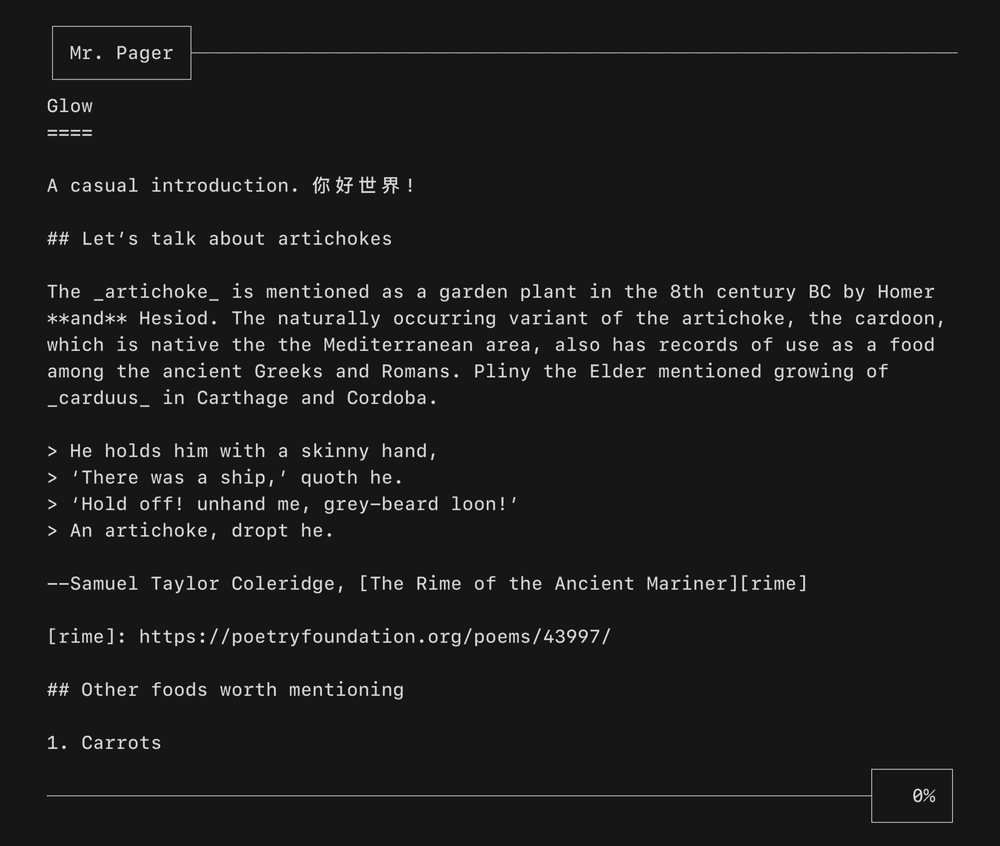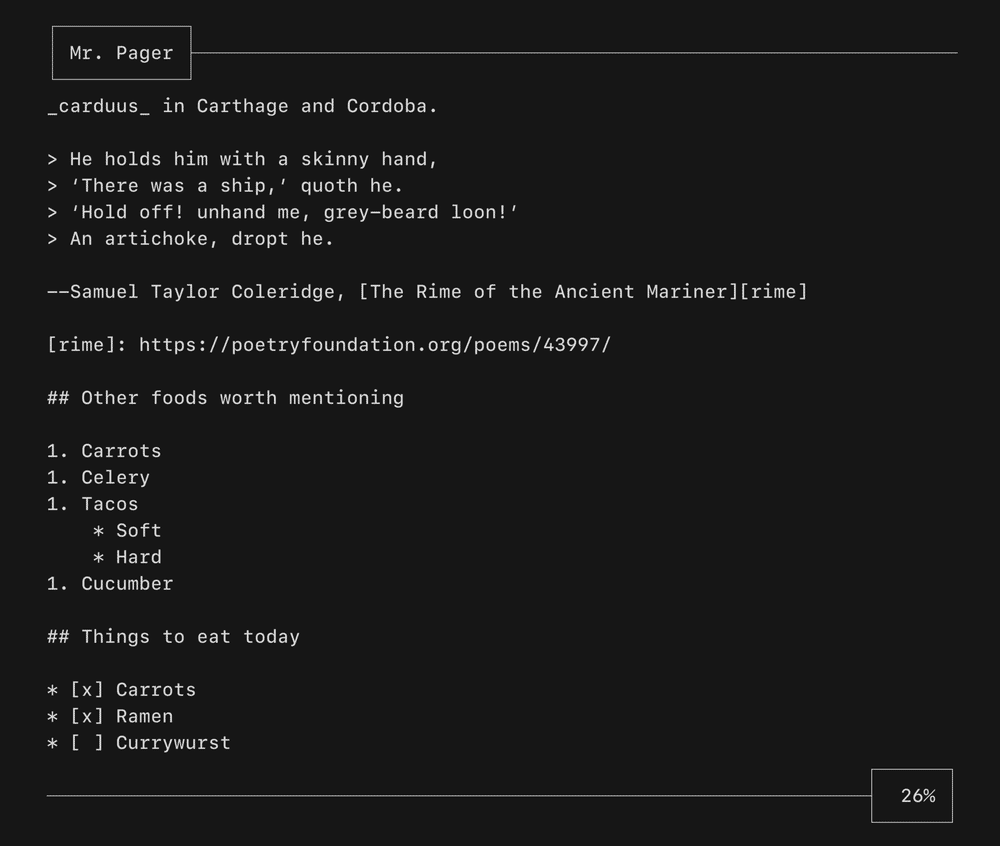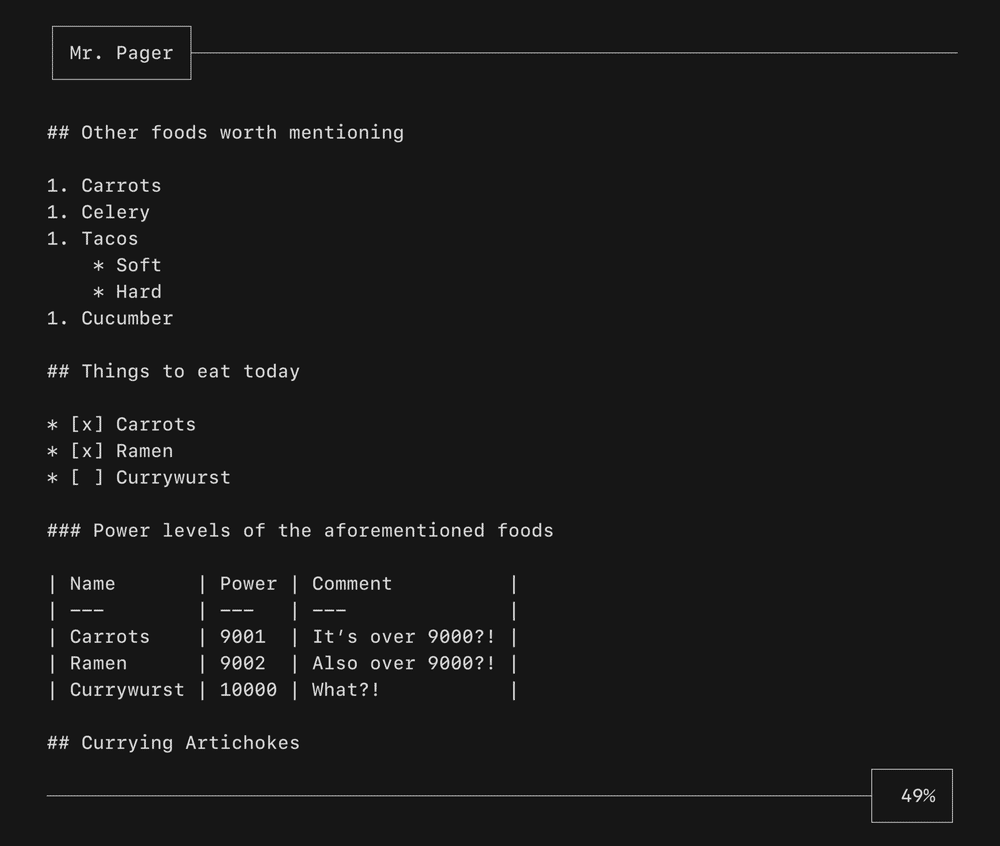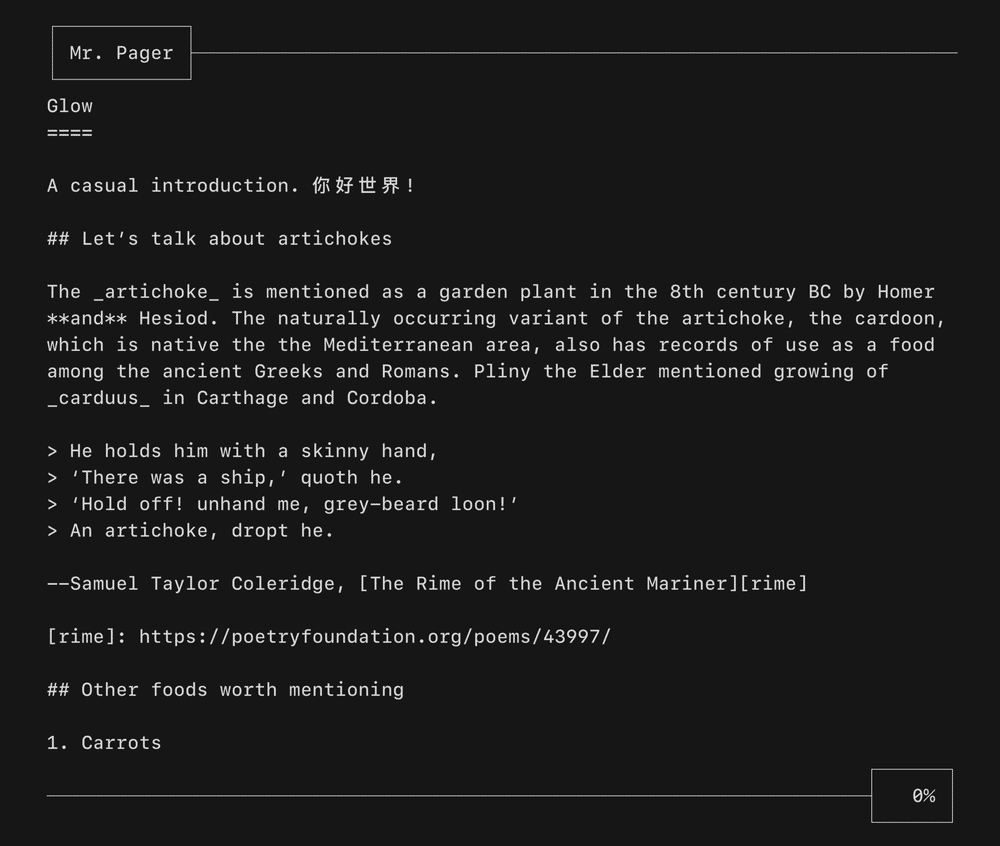
A viewport for vertically scrolling content. Optionally includes standard pager keybindings and mouse wheel support. A high performance mode is available for applications which make use of the alternate screen buffer.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"strings"
// Here we import bubbles viewport
"github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/viewport"
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
)
var (
titleStyle = func() lipgloss.Style {
b := lipgloss.RoundedBorder()
b.Right = "├"
return lipgloss.NewStyle().BorderStyle(b).Padding(0, 1)
}()
infoStyle = func() lipgloss.Style {
b := lipgloss.RoundedBorder()
b.Left = "┤"
return titleStyle.BorderStyle(b)
}()
)
type model struct {
content string
ready bool
viewport viewport.Model // Here we use it as struct prop value
}
func (m model) Init() tea.Cmd {
return nil
}
func (m model) Update(msg tea.Msg) (tea.Model, tea.Cmd) {
var (
cmd tea.Cmd
cmds []tea.Cmd
)
switch msg := msg.(type) {
case tea.KeyMsg:
if k := msg.String(); k == "ctrl+c" || k == "q" || k == "esc" {
return m, tea.Quit
}
case tea.WindowSizeMsg:
headerHeight := lipgloss.Height(m.headerView())
footerHeight := lipgloss.Height(m.footerView())
verticalMarginHeight := headerHeight + footerHeight
if !m.ready {
// Since this program is using the full size of the viewport we
// need to wait until we've received the window dimensions before
// we can initialize the viewport. The initial dimensions come in
// quickly, though asynchronously, which is why we wait for them
// here.
m.viewport = viewport.New(msg.Width, msg.Height-verticalMarginHeight)
m.viewport.YPosition = headerHeight
m.viewport.SetContent(m.content)
m.ready = true
} else {
m.viewport.Width = msg.Width
m.viewport.Height = msg.Height - verticalMarginHeight
}
}
// Handle keyboard and mouse events in the viewport
m.viewport, cmd = m.viewport.Update(msg)
cmds = append(cmds, cmd)
return m, tea.Batch(cmds...)
}
func (m model) View() string {
if !m.ready {
return "\n Initializing..."
}
return fmt.Sprintf("%s\n%s\n%s", m.headerView(), m.viewport.View(), m.footerView())
}
func (m model) headerView() string {
title := titleStyle.Render("Mr. Pager")
line := strings.Repeat("─", max(0, m.viewport.Width-lipgloss.Width(title)))
return lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Center, title, line)
}
func (m model) footerView() string {
info := infoStyle.Render(fmt.Sprintf("%3.f%%", m.viewport.ScrollPercent()*100))
line := strings.Repeat("─", max(0, m.viewport.Width-lipgloss.Width(info)))
return lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Center, line, info)
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
func main() {
// Load some text for our viewport
content, err := os.ReadFile("artichoke.md")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("could not load file:", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
p := tea.NewProgram(
model{content: string(content)},
tea.WithAltScreen(), // use the full size of the terminal in its "alternate screen buffer"
tea.WithMouseCellMotion(), // turn on mouse support so we can track the mouse wheel
)
if _, err := p.Run(); err != nil {
fmt.Println("could not run program:", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}Note
This component is well complemented with Reflow for ANSI-aware indenting and text wrapping.
How is this guide?