Components
Help
This is help snippet using bubbletea and lipgloss
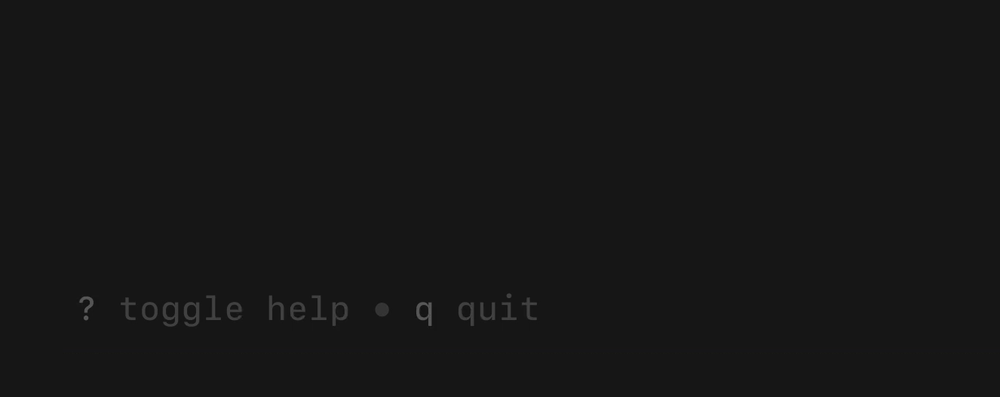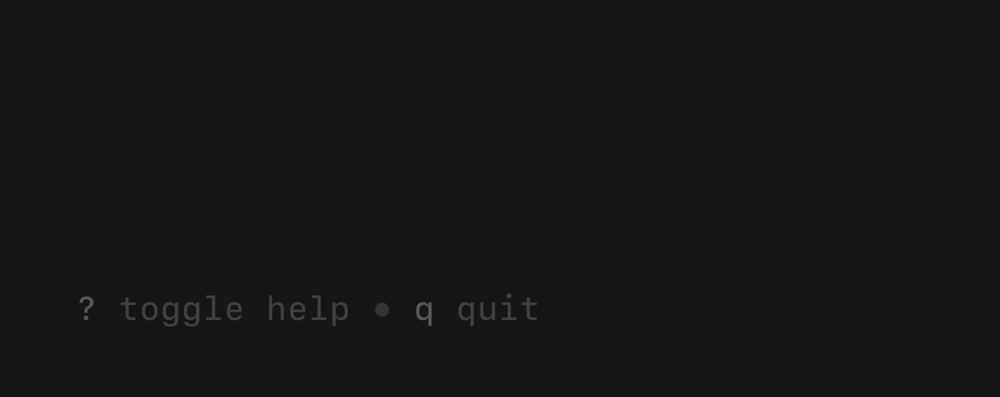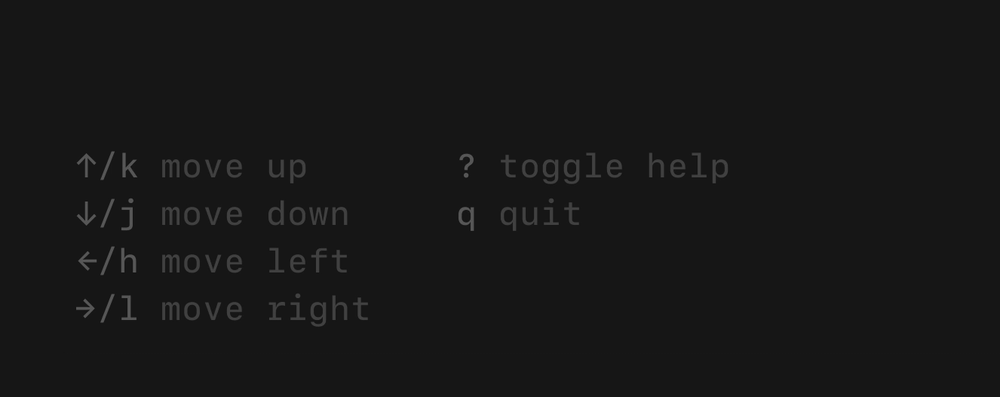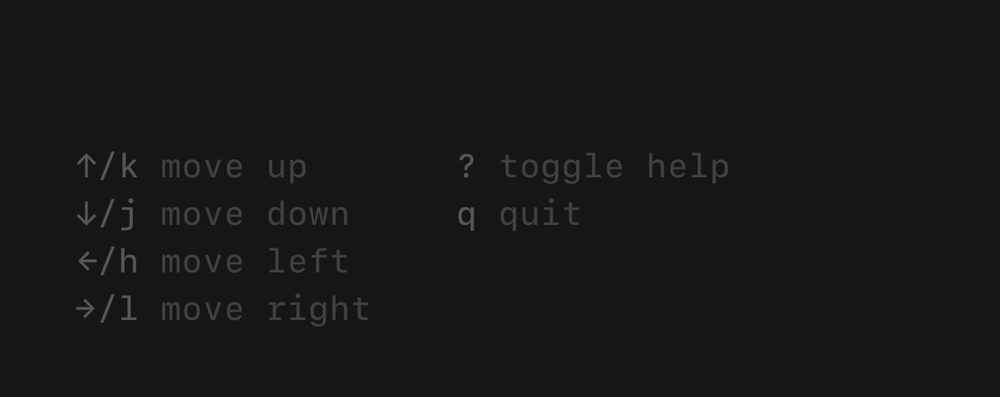
Help
A customizable horizontal mini help view that automatically generates itself from your keybindings. It features single and multi-line modes, which the user can optionally toggle between. It will truncate gracefully if the terminal is too wide for the content.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"strings"
"github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/help"
"github.com/charmbracelet/bubbles/key"
tea "github.com/charmbracelet/bubbletea"
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
)
// keyMap defines a set of keybindings. To work for help it must satisfy
// key.Map. It could also very easily be a map[string]key.Binding.
type keyMap struct {
Up key.Binding
Down key.Binding
Left key.Binding
Right key.Binding
Help key.Binding
Quit key.Binding
}
// ShortHelp returns keybindings to be shown in the mini help view. It's part
// of the key.Map interface.
func (k keyMap) ShortHelp() []key.Binding {
return []key.Binding{k.Help, k.Quit}
}
// FullHelp returns keybindings for the expanded help view. It's part of the
// key.Map interface.
func (k keyMap) FullHelp() [][]key.Binding {
return [][]key.Binding{
{k.Up, k.Down, k.Left, k.Right}, // first column
{k.Help, k.Quit}, // second column
}
}
var keys = keyMap{
Up: key.NewBinding(
key.WithKeys("up", "k"),
key.WithHelp("↑/k", "move up"),
),
Down: key.NewBinding(
key.WithKeys("down", "j"),
key.WithHelp("↓/j", "move down"),
),
Left: key.NewBinding(
key.WithKeys("left", "h"),
key.WithHelp("←/h", "move left"),
),
Right: key.NewBinding(
key.WithKeys("right", "l"),
key.WithHelp("→/l", "move right"),
),
Help: key.NewBinding(
key.WithKeys("?"),
key.WithHelp("?", "toggle help"),
),
Quit: key.NewBinding(
key.WithKeys("q", "esc", "ctrl+c"),
key.WithHelp("q", "quit"),
),
}
type model struct {
keys keyMap
help help.Model
inputStyle lipgloss.Style
lastKey string
quitting bool
}
func newModel() model {
return model{
keys: keys,
help: help.New(),
inputStyle: lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("#FF75B7")),
}
}
func (m model) Init() tea.Cmd {
return nil
}
func (m model) Update(msg tea.Msg) (tea.Model, tea.Cmd) {
switch msg := msg.(type) {
case tea.WindowSizeMsg:
// If we set a width on the help menu it can gracefully truncate
// its view as needed.
m.help.Width = msg.Width
case tea.KeyMsg:
switch {
case key.Matches(msg, m.keys.Up):
m.lastKey = "↑"
case key.Matches(msg, m.keys.Down):
m.lastKey = "↓"
case key.Matches(msg, m.keys.Left):
m.lastKey = "←"
case key.Matches(msg, m.keys.Right):
m.lastKey = "→"
case key.Matches(msg, m.keys.Help):
m.help.ShowAll = !m.help.ShowAll
case key.Matches(msg, m.keys.Quit):
m.quitting = true
return m, tea.Quit
}
}
return m, nil
}
func (m model) View() string {
if m.quitting {
return "Bye!\n"
}
var status string
if m.lastKey == "" {
status = "Waiting for input..."
} else {
status = "You chose: " + m.inputStyle.Render(m.lastKey)
}
helpView := m.help.View(m.keys)
height := 8 - strings.Count(status, "\n") - strings.Count(helpView, "\n")
return "\n" + status + strings.Repeat("\n", height) + helpView
}
func main() {
if os.Getenv("HELP_DEBUG") != "" {
f, err := tea.LogToFile("debug.log", "help")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Couldn't open a file for logging:", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
defer f.Close() // nolint:errcheck
}
if _, err := tea.NewProgram(newModel()).Run(); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Could not start program :(\n%v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}How is this guide?